Mesothelium Cancer

- The layer of flat cells, derived from the mesoderm, that lines the body cavity of the embryo. In the adult it forms the simple squamous epithelium that covers the surface of all true serous membranes (peritoneum, pericardium, pleura).
- A single layer of flattened cells forming an epithelium that lines serous cavities.
- The layer of flat cells of mesodermal origin that lines the embryonic body cavity and gives rise to the squamous cells.
- Lining cells originating in the primitive MESODERM of the developing embryo. Mesothelium occurs in the
- PERITONEUM -> peritoneal mesothelium
- PLEURA - pleura mesothelium
- PERICARDIUM - pericardium mesothelium
- as well as elsewhere in the body.
- A membrane/sac that that protects the body's major internal organs and allows them freedom of movement. The mesothelium is comprised of several regions, including the abdominal cavity , the chest cavity , and pericardium .
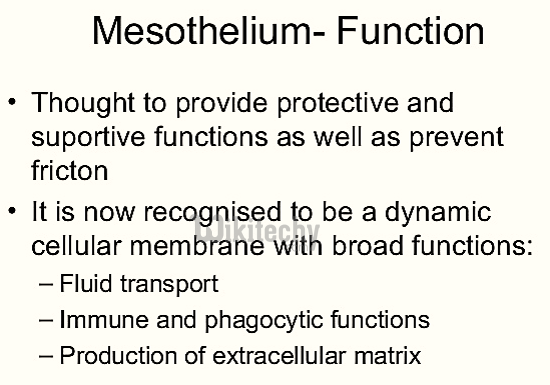
- The existence of the mesothelium was assumed to provide a slippery, non-sticky surface to protect internal organs.
- But, the mesothelium has other important functions. They are:
- The transport and movement of fluids and matter across the membrane.
- This occurs from the outer aspects of the chest and abdominal cavities to the internal organs.
- Coagulation (blood clotting)
- Healing function
- Immunity against infection as well as the spread of tumors.
