apache hive - hive mapreduce - hadoop mapreduce - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
What is Hive ?
- Hive is a data warehouse infrastructure tool to process structured data in Hadoop.
- It lives on top of Hadoop to summarize Big Data, and makes querying and analyzing easy.
- Initially Hive was developed by Facebook, later the Apache Software Foundation took it up and developed it further as an open source under the name Apache Hive.
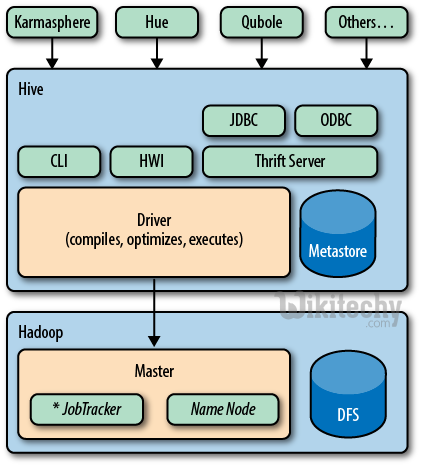
Learn hive - hive tutorial - learn hive tutorial - process in hive vs mapreduce - hive example - hive examples - hive programs
What is Mapreduce?
- MapReduce is a programming model suitable for processing of huge data.
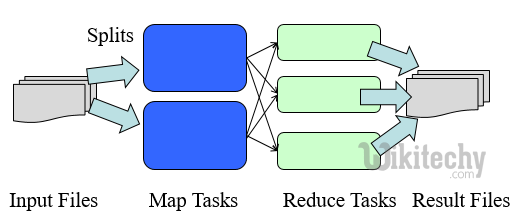
- Hadoop is capable of running MapReduce programs written in various languages:
- Java,
- Ruby,
- Python,
- and C++.
- MapReduce programs are parallel in nature, thus are very useful for performing large-scale data analysis using multiple machines in the cluster.
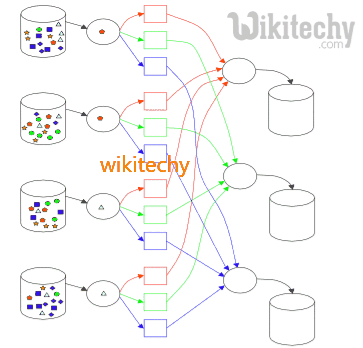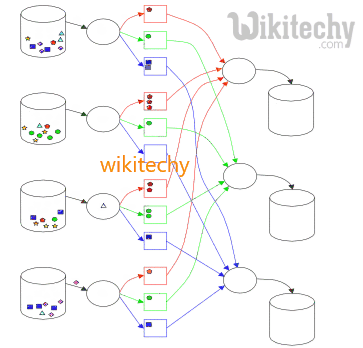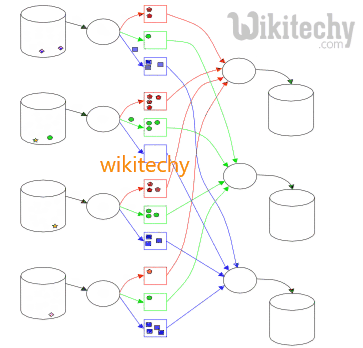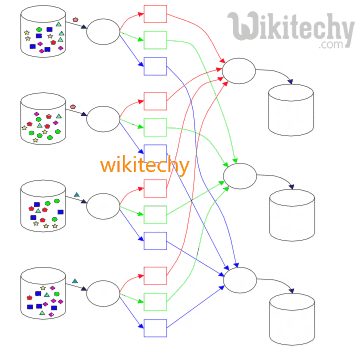
Learn hive - hive tutorial - learn hive tutorial - data sharing in hive vs map reduce - hive example - hive examples - hive programs
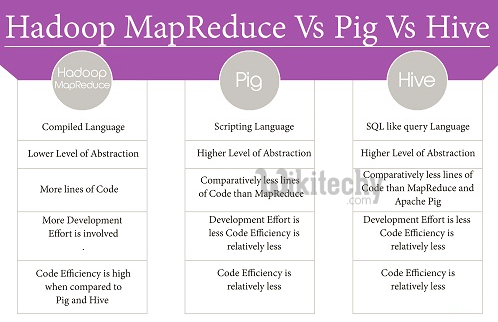
Difference between Hive and Mapreduce:
- Previous to selecting one of these two options, we must look at some of their features. Hive and Map reduce choosing some factors are,
- Type of Data
- Amount of Data
- Complexity of Code
| Feature | Hive | Map Reduce |
|---|---|---|
| Language | It Supports SQL like query language for interaction and for Data modeling |
It compiles language with two main tasks present in it. One is map task, and another one is a reducer. |
| Compiled Language | We can define these task using Java or Python Sql like Query Language | |
| Level of abstraction | Higher level of Abstraction on top of HDFS | Lower level of abstraction |
| Efficiency in Code | Comparatively lesser than Map reduce | Provides High efficiency |
| Extent of code | Less number of lines code required for execution | More number of lines of codes to be defined |
| Type of Development work required | Less Development work required | More development work needed |
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
MAPREDUCE SCRIPT :
Example - script to filter out rows to remove poor quality readings.
import re
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
(year, temp, q) = line.strip().split()
if (temp != "9999" and re.match("[01459]", q))
print "%s\t%s" % (year, temp)
hive> ADD FILE /path/to/is_good_quality.py;
hive> FROM records2
> SELECT TRANSFORM(year, temperature, quality)
> USING 'is_good)quality.py'
> AS year, temperature;
Output :
1949 111
1949 78
1950 0
1950 22
1950 -11
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - mapreduce vs pig vs hive - hive examples
Hive QL Join :
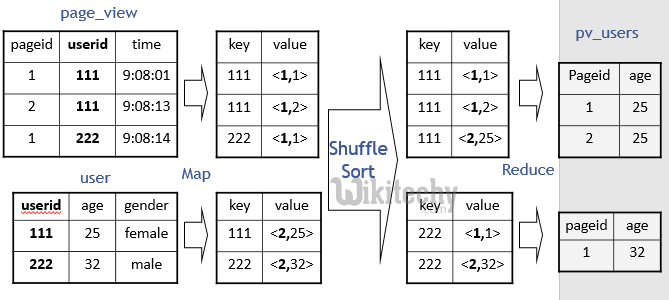
Hive QL Join - Example 1 :
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql join - hive examples
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql join map reduce - hive examples
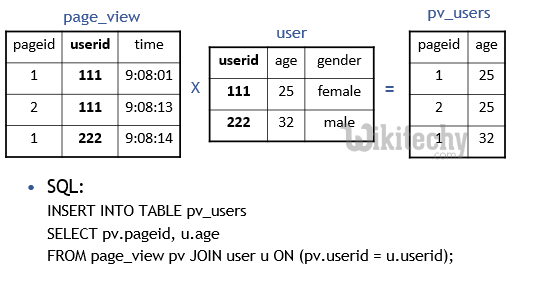
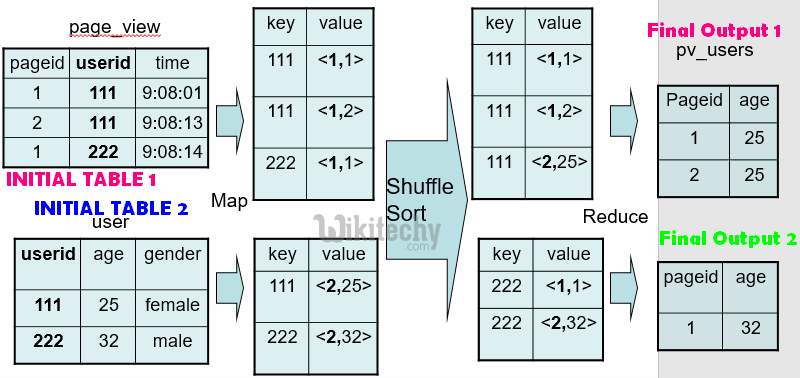
Hive QL Join - Example 2 :
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view pv
JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive mapreduce programming - hive examples
- Rightmost table streamed – whereas inner tables data is kept in memory for a given key. Use largest table as the right most table.
- hive.mapred.mode = nonstrict
- In strict mode, Cartesian product not allowed
Below is HiveQL Join, :
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE pv_users
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid) JOIN newuser x on (u.userid = x.userid);
- Same join key – merge into 1 map-reduce job – true for any number of tables with the same join key. 1 map-reduce job instead of ‘n’
- The merging happens for OUTER joins also
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid) JOIN newuser x on (u.age = x.age);
Different join keys – 2 map-reduce jobs Same as:
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
SELECT x.pageid, x.age
FROM tmptable x JOIN newuser y on (x.age = y.age);
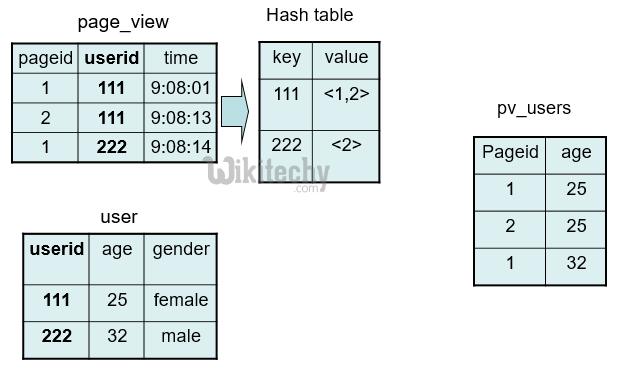
Join Optimization - Map Joins :
SELECT /*+ MAPJOIN(pv) */ pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view pv JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hiveql map join and join optimization - hive examples
- Optimization phase
- n-way map-join if (n-1) tables are map side readable
- Mapper reads all (n-1) tables before processing the main table under consideration
- Map-side readable tables are cached in memory and backed by JDBM persistent hash tables
Parameters for Join Optimization and Map Joins :
- hive.join.emit.interval = 1000
- hive.mapjoin.size.key = 10000
- hive.mapjoin.cache.numrows = 10000
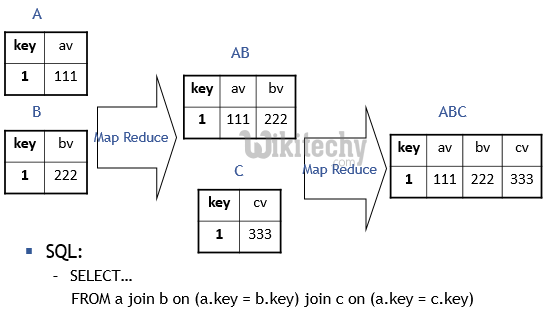
Hive QL Multiple Tables Join with Map Reduce - Example 3 :
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql multiple table join map reduce - hive examples
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
Hive QL – Group By - Optimizations :
FROM pv_users
GROUP BY pageid, age;
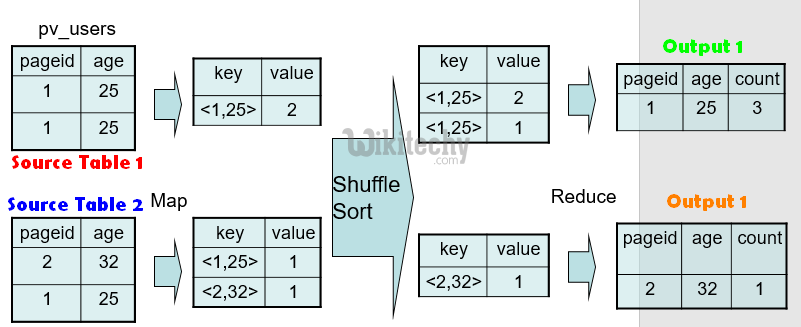
- Map side partial aggregations
- Hash-based aggregates
- Serialized key/values in hash tables
- 90% speed improvement on Query SELECT count(1) FROM t;
- Load balancing for data skew
Parameters for Group by Optimization :
- hive.map.aggr = true
- hive.groupby.skewindata = false
- hive.groupby.mapaggr.checkinterval = 100000
- hive.map.aggr.hash.percentmemory = 0.5
- hive.map.aggr.hash.min.reduction = 0.5
