pointer to array | array of pointers | C++ Pointers and Arrays - Learn C++ - C++ Tutorial - C++ programming

Learn c++ - c++ tutorial - pointer-to-array-in-c++ - c++ examples - c++ programs
- In this article, you'll learn about the relation between arrays and pointers, and use them efficiently in your program.
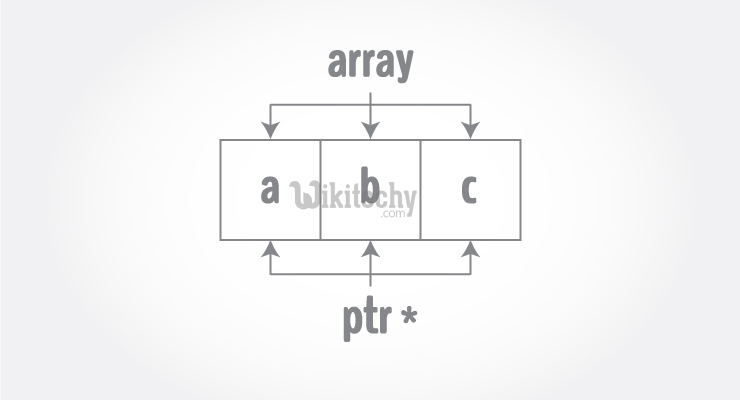
- Pointers are the variables that hold address. Not only can pointers store address of a single variable, it can also store address of cells of an array.
- Consider this example:
int* ptr;
int a[5];
ptr = &a[2]; // &a[2] is the address of third element of a[5].

- Suppose, pointer needs to point to the fourth element of an array, that is, hold address of fourth array element in above case.
- Since ptr points to the third element in the above example, ptr + 1 will point to the fourth element.
- You may think, ptr + 1 gives you the address of next byte to the ptr. But it's not correct.
- This is because pointer ptr is a pointer to an int and size of int is fixed for a operating system (size of int is 4 byte of 64-bit operating system). Hence, the address between ptrand ptr + 1 differs by 4 bytes.
- If pointer ptr was pointer to char then, the address between ptr and ptr + 1 would have differed by 1 byte since size of a character is 1 byte.
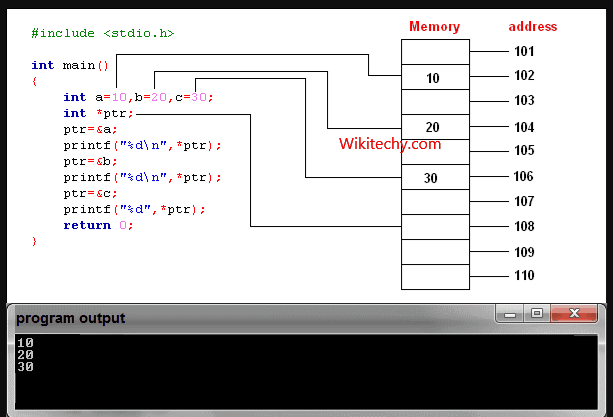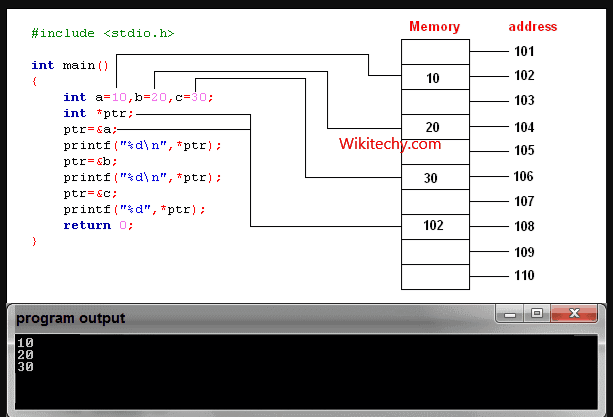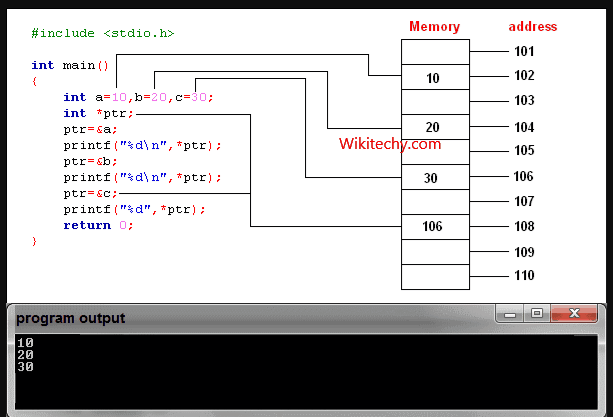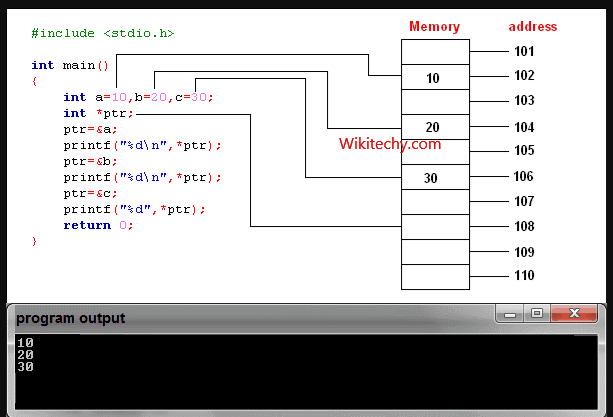
learn c++ tutorials - pointers in c++ Example
Reference operator (&) as discussed above gives the address of a variable.
- To get the value stored in the memory address, we use the dereference operator (*).
- For example: If a number variable is stored in the memory address 0x123, and it contains a value 5.
- The reference (&) operator gives the value 0x123, while the dereference (*) operator gives the value 5.
- Note: The (*) sign used in the declaration of C++ pointer is not the dereference pointer. It is just a similar notation that creates a pointer.
Example 1: C++ Pointers and Arrays
- C++ Program to display address of elements of an array using both array and pointers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float arr[5];
float *ptr;
cout << "Displaying address using arrays: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cout << "&arr[" << i << "] = " << &arr[i] << endl;
}
// ptr = &arr[0]
ptr = arr;
cout<<"\nDisplaying address using pointers: "<< endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cout << "ptr + " << i << " = "<< ptr + i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Output
Displaying address using arrays:
&arr[0] = 0x7fff5fbff880
&arr[1] = 0x7fff5fbff884
&arr[2] = 0x7fff5fbff888
&arr[3] = 0x7fff5fbff88c
&arr[4] = 0x7fff5fbff890
Displaying address using pointers:
ptr + 0 = 0x7fff5fbff880
ptr + 1 = 0x7fff5fbff884
ptr + 2 = 0x7fff5fbff888
ptr + 3 = 0x7fff5fbff88c
ptr + 4 = 0x7fff5fbff890- In the above program, a different pointer ptr is used for displaying the address of array elements arr.
- But, array elements can be accessed using pointer notation by using same array name arr. For example:
int arr[3];
&arr[0] is equivalent to arr
&arr[1] is equivalent to arr + 1
&arr[2] is equivalen to arr + 2
Example 2: Pointer and Arrays
- C++ Program to display address of array elements using pointer notation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float arr[5];
cout<<"Displaying address using pointers notation: "<< endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cout << arr + i <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Output
Displaying address using pointers notation:
0x7fff5fbff8a0
0x7fff5fbff8a4
0x7fff5fbff8a8
0x7fff5fbff8ac
0x7fff5fbff8b0
- You know that, pointer ptr holds the address and expression *ptr gives the value stored in the address.
- Similarly, you can get the value stored in the pointer ptr + 1 using *(ptr + 1).
- Consider this code below:
int ptr[5] = {3, 4, 5, 5, 3};
- &ptr[0] is equal to ptr and *ptr is equal to ptr[0]
- &ptr[1] is equal to ptr + 1 and *(ptr + 1) is equal to ptr[1]
- &ptr[2] is equal to ptr + 2 and *(ptr + 2) is equal to ptr[2]
- &ptr[i] is equal to ptr + i and *(ptr + i) is equal to ptr[i]
Example 3: C++ Pointer and Array
- C++ Program to insert and display data entered by using pointer notation.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float arr[5];
// Inserting data using pointer notation
cout << "Enter 5 numbers: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cin >> *(arr + i) ;
}
// Displaying data using pointer notation
cout << "Displaying data: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cout << *(arr + i) << endl ;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter 5 numbers: 2.5
3.5
4.5
5
2
Displaying data:
2.5
3.5
4.5
5
2
