oauth tutorial - OAuth Client Credentials - oauth2 tutorial - oauth authentication
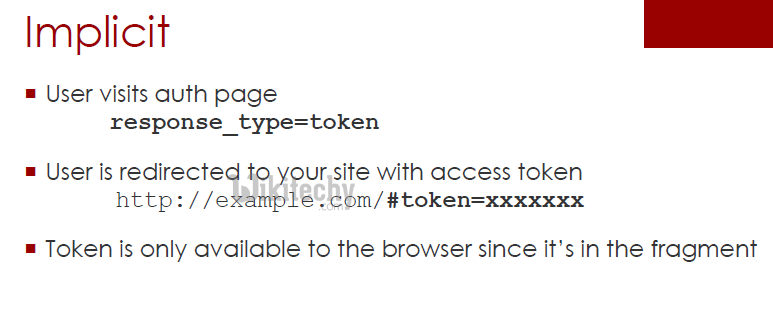
What is Client Credentials in OAuth 2.0?

- The client credentials are used as an authorization grant when the client is the resource owner to protected resources which is done under the control of the client.
- The client credentials requests an access token only with the help of client credentials.
- The client credentials authorization flow is used to acquire an access token in order to authorize API requests.
- The Client Credentials grant is used when the applications request an access token to access their own resources, which is done based on the user
- Using client credentials authorization, access token is acquired which grants permission for the client application to search and get catalog documents.
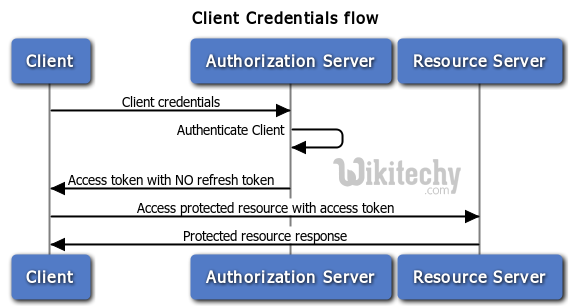
- The diagram which is given below describes the client credentials flow
Learn OAuth 2.0 - OAuth 2.0 tutorial - process of client credentials flow in oauth - OAuth 2.0 examples - OAuth 2.0 programs
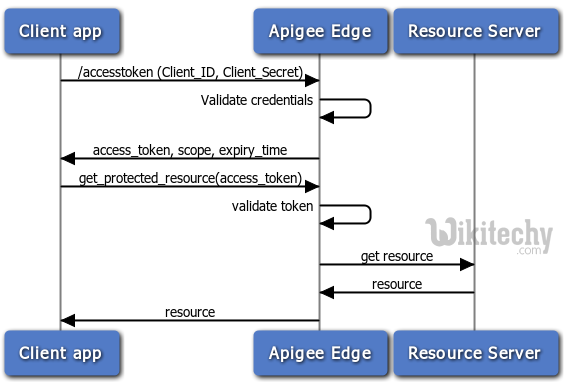
Description of the diagram:
- The client sends the client credentials with the authorization server authenticates with the authorization server
- The authorization server authenticates the client and provides access token with no refresh token and send it back to the client
- The client access protected resource with the access token in the resource server
- Hence the resource sends back a protected resource response to the client
- The table which is given below lists the concepts of Client Credentials.
| Sr.No. | Concept & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Obtaining End-User Authorization
The authorization end point is typically URI on the authorization server in which the resource owner logs in and permits to access the data to the client application. |
| 2 | Authorization Response The authorization response can be used to get the access token for accessing the owner resources in the system using the authorization code. |
| 3 | Error Response and Codes The authorization server responds with a HTTP 400 or 401 (bad request) status codes, if an error occurs during authorization. |
Client Credentials Grant flow
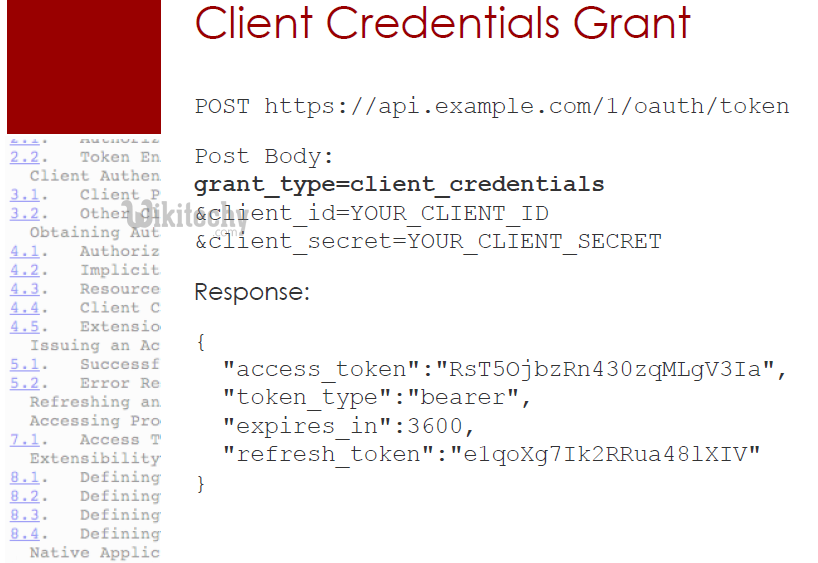
- The Client Credentials grant is suitable for machine-to-machine authentication The client Credentials grant sends a POST request with parameters which are given below to the authorization server:
- grant_type is a grant with the value client_credentials
- client_id is a client_id which is given
- Client_secret is a client’s secret which is used to redirect the URL.
- Scope is done with a space-limited list of requested scope permissions.
- The Client Credentials grant will respond with a JSON object with parameters which are given below to the authorization server:
- token_type is given with the value Bearer
- expires_in with an integer represents the TTL of the access token
- access token is a JWT signed with the authorization server’s private key
Learn OAuth 2.0 - OAuth 2.0 tutorial - process of client credentials grant flow in oauth - OAuth 2.0 examples - OAuth 2.0 programs
Client Credentials Grant Request
- The client credentials Grant Request makes a request to the authorization server, including the HTTP basic authentication header and optionally a client assertion.
- The client credentials Grant Request can use a generated client assertion or build a new assertion client.
- Hence the client credentials grant request contains the parameters which are given below:
| grant_type | It is required and must be set to client_credentials. |
| scope | It is optional and also known as the scope of the authorization. |
Client Credentials Grant Response
- The Client Credentials Grant Response authenticates the client based on the authorization header or assertion.
- If the client credentials Grant Response is authenticated, then the client gets an access token as a grant response.
- The client credentials grant response contains the parameters which are given below:
{ "access_token" : "...",
"token_type" : "...",
"expires_in" : "...",
}
click below button to copy the code. By - oauth tutorial - oauth2 tutorial - team
- The access_token is the access token which is assigned by the authorization server.
- The token_type is a type of token which is assigned by the authorization server.
- The expires_in is a number of seconds after which the access token expires, and is no longer valid.
- A refresh token should not be included for this type of authorization request.
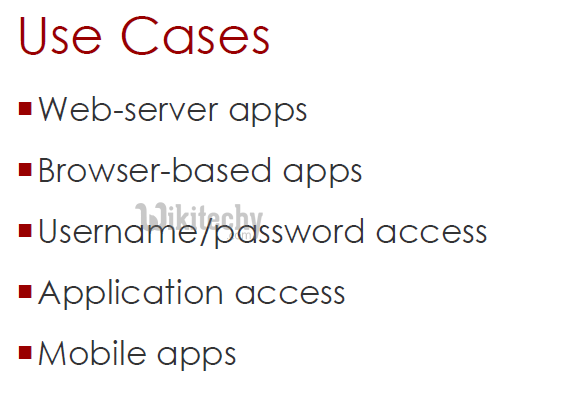
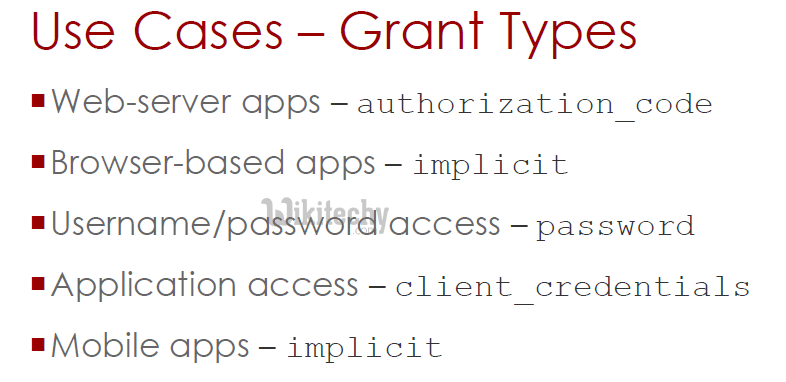
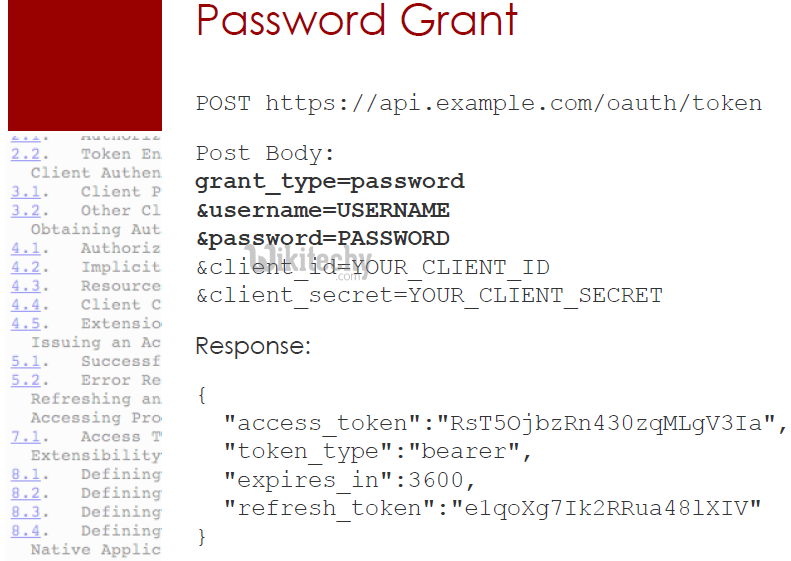
Username/Password - Password Grant


Application Access - Client Credentials Grant
Mobile Apps - Implicit Grant
Redirect back to your app

Grant Type Review