C# Type Casting - Type Casting in C# with Examples
C# Type Casting - Type Casting in C# with Examples
- If the variable of one data type is changed to another data type is known as the Type Casting.
- Manually we can change the type of data, according to our needs.
- At the time of the compilation, C# is a statically-typed i.e., after the declaration of the variable, we cannot declare it again.
- The value of the variable cannot be assigned to another type of variable unless we implicitly change the type of the variable.
Types of Type Casting
Implicit Conversion
- There is no need for the special syntax, for the implicit conversion.
- This type of conversion is safe because, in this conversion, there is not any loss of the data.
- During implicit conversion include the conversion of the small type to large integral types, and from the derived class to the base class conversion.
Sample Code
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class SumProgramme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int value1 = 567;
int value2 = 765;
long summation;
summation = value1 + value2;
Console.WriteLine("summation = " + summation);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output

Explicit Conversion
- Explicit conversion will be done with the cast operator () and also includes the conversion of the base-class instance to the derived class.
- If the conversion is not succeeded, we will do the casting when there is the situation of the data loss.
- The example of the casting is the conversion of the numeric type to the small range or less precision.
Sample Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp2
{
class ProgramExplicit
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double db = 7896.45;
int xy;
// here we do the cast double to int.
xy = (int)db;
Console.WriteLine(xy);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output
7896User-defined Conversion
- We can do this conversion by defining the method and we can use the technique to enable the explicit-implicit conversion between the custom type.
- In which does not have any relationship with the base-class or derived-class.
Sample Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System. Linq;
using System. Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace UserDefinedConversion
{
class Program
{
public struct ImperialMeasurement
{
public float feet;
public ImperialMeasurement(float r)
{
this.feet = r;
}
public static explicit operator ImperialMeasurement(int m)
{
float ConversionResult = 3.28f * m;
ImperialMeasurement temp = new ImperialMeasurement(ConversionResult);
return temp;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
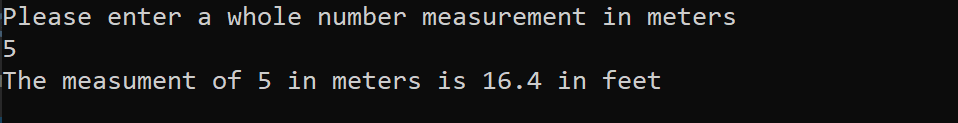
Console.WriteLine("Please enter a whole number measurement in meters");
int nm = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
ImperialMeasurement im = (ImperialMeasurement)nm;
Console.WriteLine($"The measument of {nm} in meters is {im.feet} in feet ");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output