java tutorial - Java LinkedList class - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
Learn Java - Java tutorial - Java linked list - Java examples - Java programs
Java LinkedList class uses doubly linked list to store the elements. It provides a linked-list data structure. It inherits the AbstractList class and implements List and Deque interfaces.
The important points about Java LinkedList are:
- Java LinkedList class can contain duplicate elements.
- Java LinkedList class maintains insertion order.
- Java LinkedList class is non synchronized.
- In Java LinkedList class, manipulation is fast because no shifting needs to be occurred.
- Java LinkedList class can be used as list, stack or queue.
Learn java - java tutorial - linkedlist - java examples - java programs
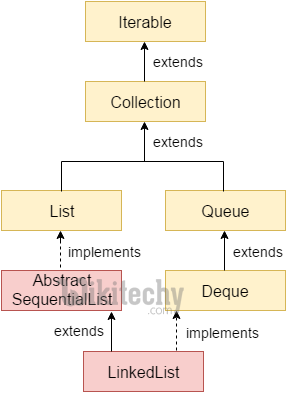
Hierarchy of LinkedList class
- As shown in above diagram, Java LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList class and implements List and Deque interfaces.
Doubly Linked List
In case of doubly linked list, we can add or remove elements from both side.

Learn java - java tutorial - doubly linked list - java examples - java programs
LinkedList class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.LinkedList class.
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>,
Deque<E>,
Cloneable,
Serializable click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Constructors of Java LinkedList
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | It is used to construct an empty list. |
| LinkedList(Collection c) | It is used to construct a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator. |
Methods of Java LinkedList
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void add(int index, Object element) | It is used to insert the specified element at the specified position index in a list. |
| void addFirst(Object o) | It is used to insert the given element at the beginning of a list. |
| void addLast(Object o) | It is used to append the given element to the end of a list. |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of elements in a list |
| boolean add(Object o) | It is used to append the specified element to the end of a list. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It is used to return true if the list contains a specified element. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It is used to remove the first occurence of the specified element in a list. |
| Object getFirst() | It is used to return the first element in a list. |
| Object getLast() | It is used to return the last element in a list. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
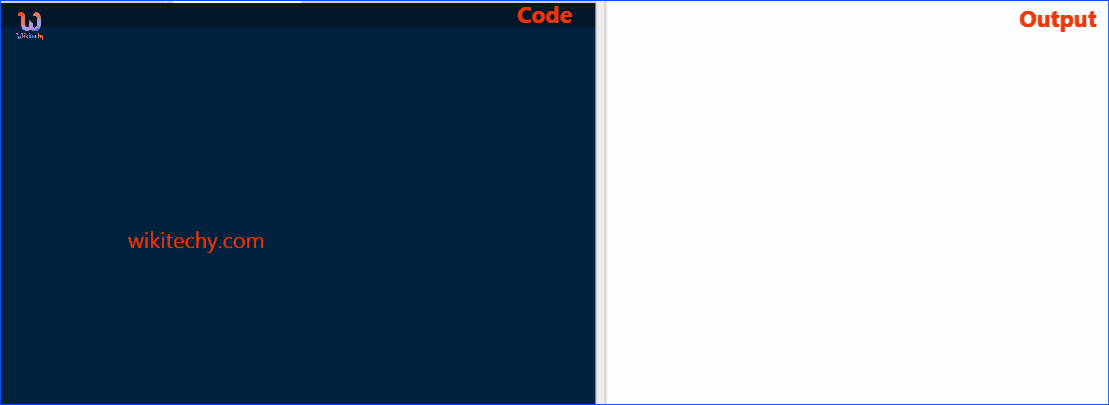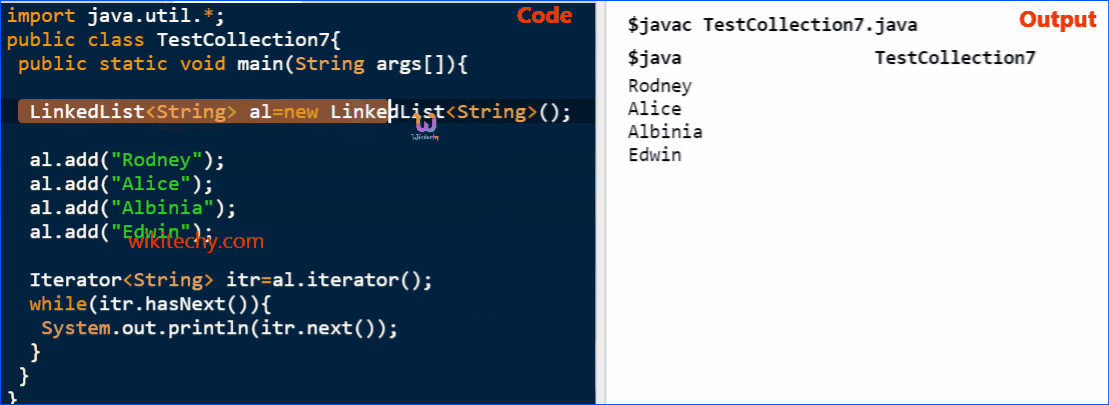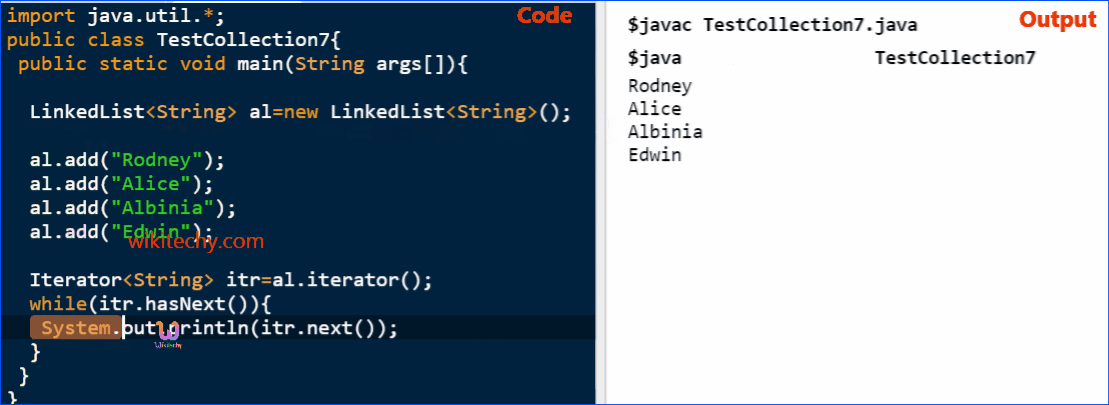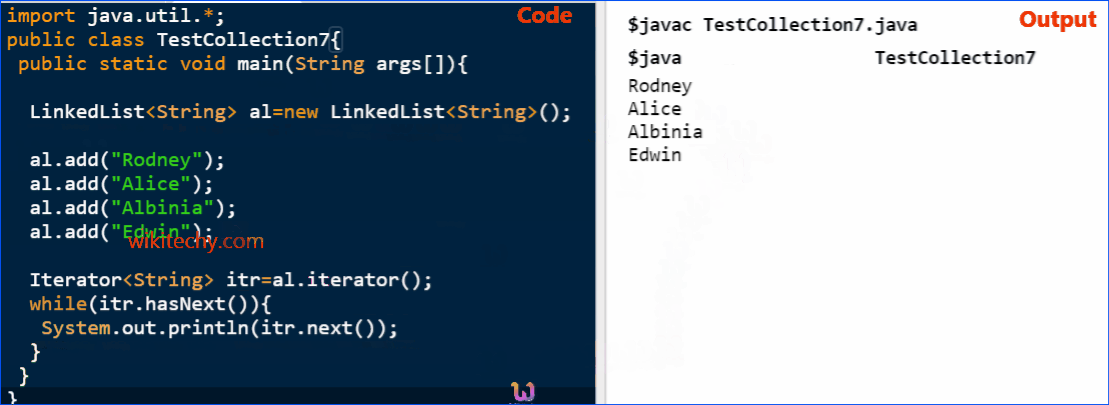
Java LinkedList Example
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollection7{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> al=new LinkedList<String>();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Ajay");
Iterator<String> itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
AjayJava LinkedList Example: Book
import java.util.*;
public class Book {
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating list of Books
List<Book> list=new LinkedList<Book>();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Let us C","Yashwant Kanetkar","BPB",8);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Data Communications & Networking","Forouzan","Mc Graw Hill",4);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Operating System","Galvin","Wiley",6);
//Adding Books to list
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
//Traversing list
for(Book b:list){
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+" "+b.quantity);
}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
102 Data Communications & Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6