java tutorial - What is the difference between Implements Runnable and Extends Thread | Java Runnable Vs Extends Thread - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
Difference between Implements Runnable and Extends Thread
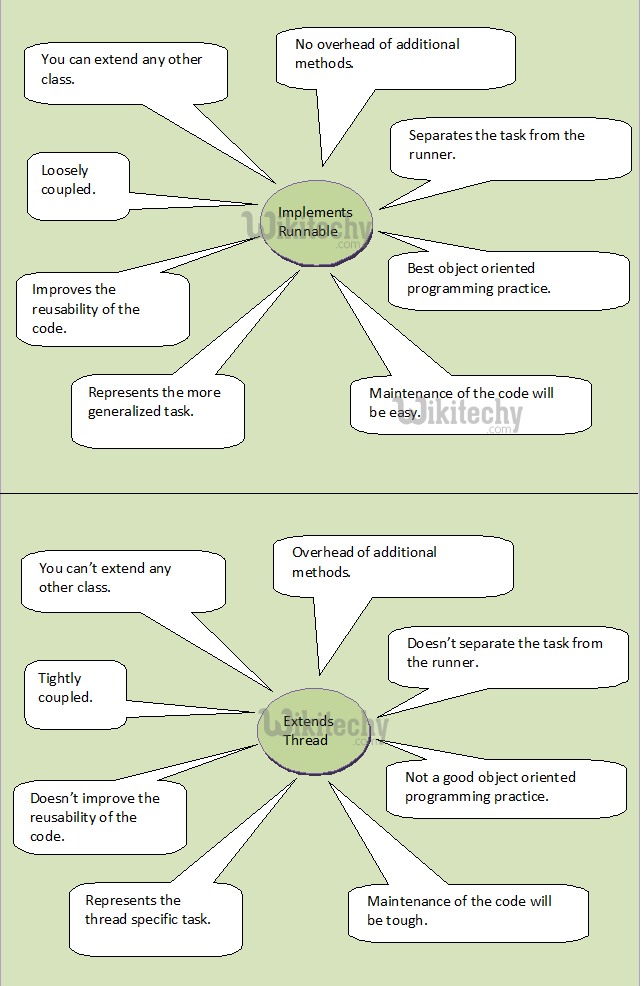
| Features | Implements Runnable | Extends Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Inheritance Limitation | Implementing the Runnable interface gives you the choice to extend any class that you like, although still define behavior that will be run by separate thread. | The drawback with "extends Thread" approach is that if you extend Thread, you cannot extend anything else. Java does not support multiple inheritances. In reality, you do not need Thread class behavior, since in order to use a thread you need to instantiate one anyway. |
| Overhead Of Additional Methods | You will remove this overhead by implementing the Runnable interface. | If you extend Thread class, every methods of Thread class will be inheriting to your class which you may not need. This will cause cause additional overhead. |
| Logical Separation Of Task From The Runner | If you implement Runnable interface, it will separate actual task from the runner. | Runnable interface represents only the task and you can pass this task to any type of runner, either a thread or any executors. |
| Best Object Oriented Design Practice | To implement Runnable will be the best object oriented design practice. | In object oriented programming (OOP), extending a class means modifying or improving the existing class. If you are not improving the class, then it is not a good practice to extend it. |
| Loosely Coupled Vs Tightly coupled | "implements Runnable" that makes the code loosely-coupled as well as ease to read. Since the code is split into two classes. Thread class for the thread specific code and then your Runnable implementation class for your job that must be run by a thread code. | "extends Thread" makes the code tightly coupled . Single class contains the thread code as well as the job that needs to be done by the thread. |
| Reusability | Here "implements Runnable”, we are creating a different Runnable class for a particular behavior job (if the work you want to be done is job). It gives us the freedom to reuse the particular behavior job whenever necessary. | "extends Thread" contains both thread and job specific behavior code. Hence once thread completes execution, it cannot be restart again. |
| Specialization Vs Generalization | “Implements Runnable” gives more generalized version of the task applicable to many threads. | “Extends Thread” gives more specialized code. Because, it defines the thread specific task. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance of the code will be easy. | Maintenance of the code will be time consuming. |
| Example | public class RunnableExample implements Runnable { public void run() { System.out.println("Alive is awesome"); } } | public class ThreadExample extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println(" Love Yourself "); } } |
Learn Java - Java tutorial - runnable vs thread - Java examples - Java programs
