java tutorial - Java Networking - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
- Java Networking is a concept of connecting two or more computing devices together so that we can share resources.
- Java socket programming provides facility to share data between different computing devices.
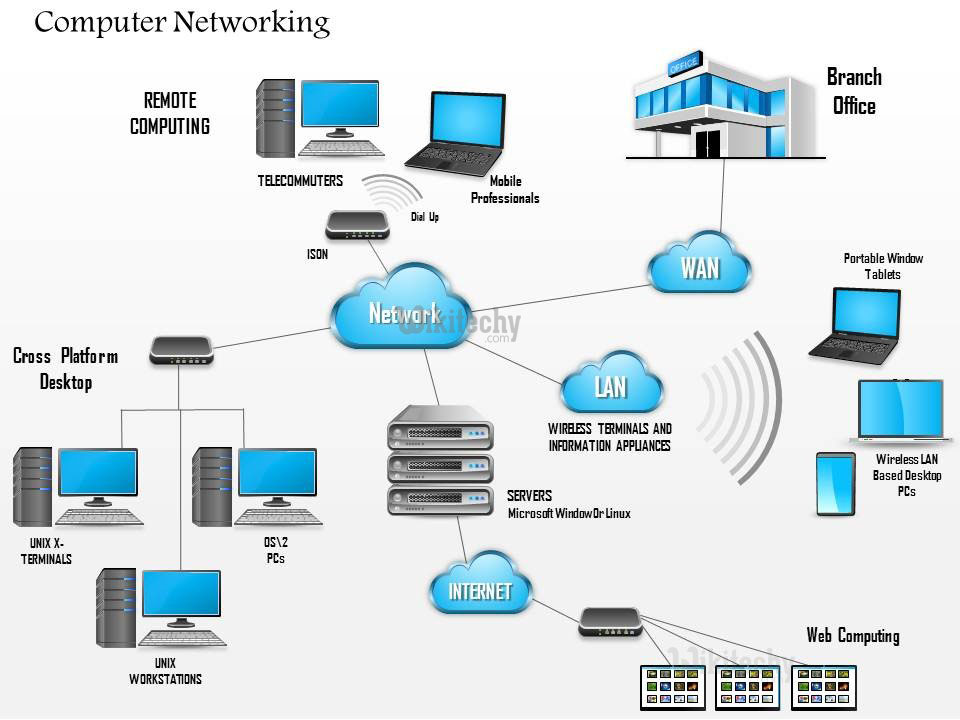
Learn Java - Java tutorial - Java Networking - Java examples - Java programs
Advantage of Java Networking
- sharing resources
- centralize software management
Java Networking Terminology
- The widely used java networking terminologies are given below:
- IP Address
- Protocol
- Port Number
- MAC Address
- Connection-oriented and connection-less protocol
- Socket
IP Address
- IP address is a unique number assigned to a node of a network e.g. 192.168.0.1 . It is composed of octets that range from 0 to 255.
- It is a logical address that can be changed.
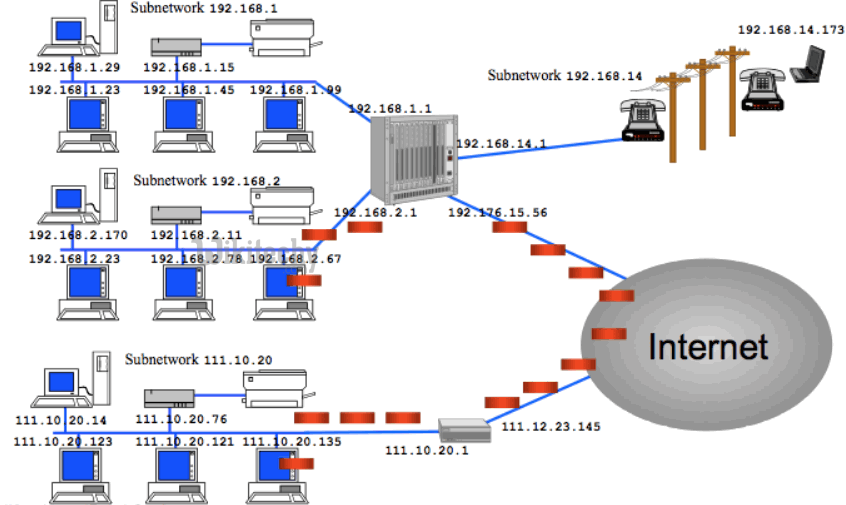
Learn Java - Java tutorial - ip address in java networking - Java examples - Java programs
Protocol
- A protocol is a set of rules basically that is followed for communication. For example:
- TCP
- FTP
- Telnet
- SMTP
- POP etc.
Port Number
- The port number is used to uniquely identify different applications. It acts as a communication endpoint between applications.
- The port number is associated with the IP address for communication between two applications.
MAC Address
- MAC (Media Access Control) Address is a unique identifier of NIC (Network Interface Controller).
- A network node can have multiple NIC but each with unique MAC.
Connection-oriented and connection-less protocol
- In connection-oriented protocol, acknowledgement is sent by the receiver. So it is reliable but slow. The example of connection-oriented protocol is TCP.
- But, in connection-less protocol, acknowledgement is not sent by the receiver. So it is not reliable but fast. The example of connection-less protocol is UDP.
Socket
- A socket is an endpoint between two way communication.
