Cyber Security Standards
Cyber Security Standards
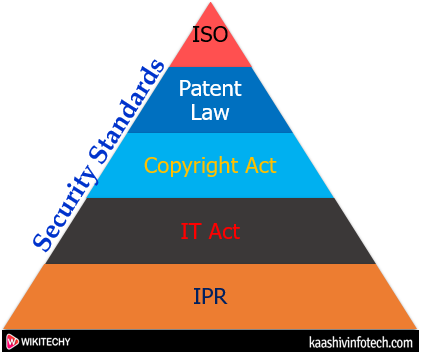
Security Standards
A security standard is "a published specification that establishes a common language, and contains a technical specification or other precise criteria and is designed to be used consistently, as a rule, a guideline, or a definition."
The goal of security standards is to improve the security of information technology (IT) systems, networks, and critical infrastructures. The Well-Written cyber security standards enable consistency among product developers and serve as a reliable standard for purchasing security products.
1. ISO
- These standards provide a world-class specification for products, services and computers, to ensure quality, safety and efficiency.
- ISO standard is officially established On 23 February 1947. It is an independent, non-governmental international organization. Today, it has a membership of 162 national standards bodies and 784 technical committees and subcommittees to take care of standards development.
- ISO has published over 22336 International Standards and its related documents which covers almost every industry, from information technology, to food safety, to agriculture and healthcare.
ISO 27000 Series
- Developed by the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electro technical Commission to provide a globally recognized framework for best information security management.
- The cyber-attacks are growing day by day making hackers a constant threat to any industry that uses technology.
- The ISO 27000 series can be categorized into many types. They are-
- ISO 27001 - This standard allows us to prove the clients and stakeholders of any organization to managing the best security of their confidential data and information.
- ISO 27000 - This standard provides an explanation of terminologies used in ISO 27001.
- ISO 27002 - This standard provides guidelines for organizational information security standards and information security management practices. It includes the selection, implementation, operating and management of controls taking into consideration the organization's information security risk environment(s).
- ISO 27005 - This standard supports the general concepts specified in 27001. It is designed to provide the guidelines for implementation of information security based on a risk management approach. This standard is capable for all kind of organizations such as non-government organization, government agencies, and commercial enterprises.
- ISO 27032 - It is the international Standard which focuses explicitly on cyber security.
Read Also
2. IT Act
- The IT Act is based on the United Nations Model Law on E-Commerce 1996 recommended by the General Assembly of United Nations. This act is also used to check misuse of cyber network and computer in India.
- IT Act 2000 has 13 chapters, 94 sections and 4 schedules. The first 14 sections concerning digital signatures and other sections deal with the certifying authorities who are licensed to issue digital signature certificates, sections 43 to 47 provides penalties and compensation, section 48 to 64 deal with appeal to high court, sections 65 to 79 deal with offences, and the remaining section 80 to 94 deal with miscellaneous of the act.
3. Copyright Act
- The copyright law has been enacted to balance the use and reuse of creative works against the desire of the creators of art, literature, music and monetize their work by controlling who can make and sell copies of the work.
- The copyright act covers the following-
- Rights of copyright owners
- Works eligible for protection
- Duration of copyright
- Who can claim copy right
- The copyright act does not cover the following-
- Ideas, procedures, methods, processes, concepts, systems, principles, or discoveries
- Works that are not fixed in a tangible form
- Familiar symbols or designs
- Titles, names, short phrases, and slogans
- Mere variations of typographic ornamentation, lettering, or coloring
4. Patent Law
- Patent law is a law that deals with new inventions. In general, a patent is a right that can be granted if an invention is:
- Not a natural object or process
- New
- Useful
- Not obvious.
5. IPR
- Intellectual property rights is a right that allow creators, or owners of patents, trademarks or copyrighted works to benefit from their own plans, ideas, or other intangible assets or investment in a creation. It provides for the right to benefit from the protection of moral and material interests resulting from authorship of scientific, literary or artistic productions.
