In Python 2, both str and bytes are the same typeByte objects whereas in Python 3 Byte objects, defined in Python 3 are “sequence of bytes” and similar to “unicode” objects from Python 2. However, there are many differences in strings and Byte objects. Some of them are depicted below:
`
Learn Python - Python tutorial - python encode - Python examples - Python programs
- Byte objects are sequence of Bytes, whereas Strings are sequence of characters.
- Byte objects are in machine readable form internally, Strings are only in human readable form.
- Since Byte objects are machine readable, they can be directly stored on the disk. Whereas, Strings need encoding before which they can be stored on disk.
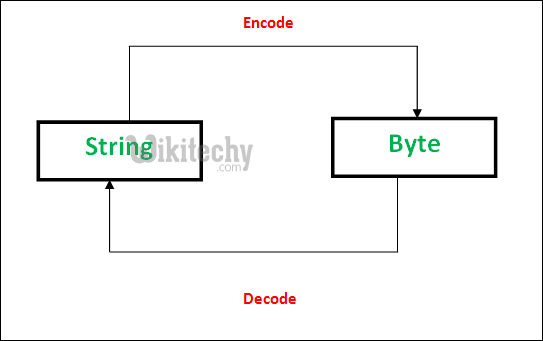
There are methods to convert a byte object to String and String to byte objects.
PNG, JPEG, MP3, WAV, ASCII, UTF-8 etc are different forms of encodings. An encoding is a format to represent audio, images, text, etc in bytes. Converting Strings to byte objects is termed as encoding. This is necessary so that the text can be stored on disk using mapping using ASCII or UTF-8 encoding techniques.
This task is achieved using encode(). It take encoding technique as argument. Default technique is “UTF-8” technique.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstate String encoding
# initialising a String
a = 'Wikitechy'
# initialising a byte object
c = b'Wikitechy'
# using encode() to encode the String
# encoded version of a is stored in d
# using ASCII mapping
d = a.encode('ASCII')
# checking if a is converted to bytes or not
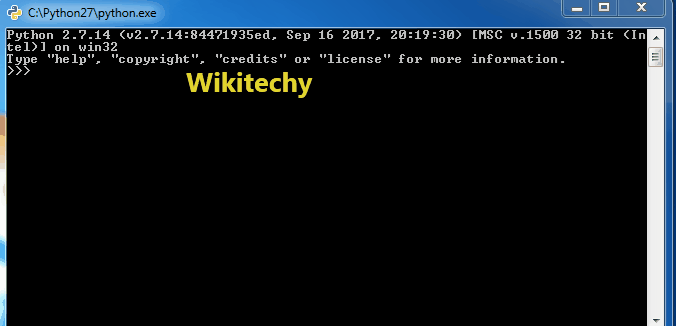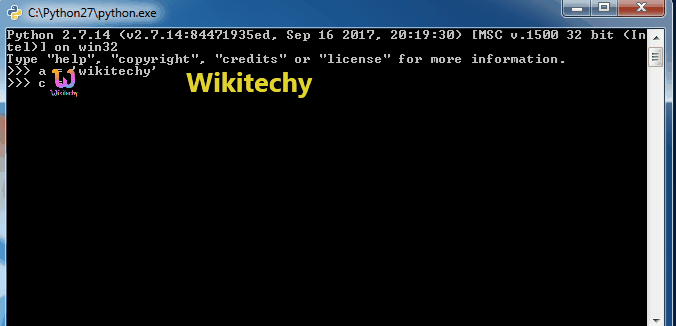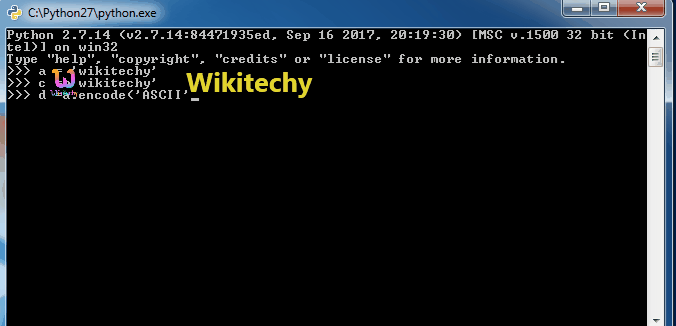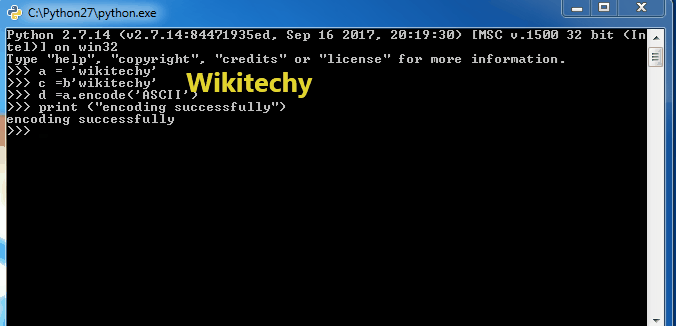
if (d==c):
print ("Encoding successful")
else : print ("Encoding Unsuccessful")python tutorial - Output :
Encoding successful
Similarly, Decoding is process to convert a Byte object to String. It is implemented using decode() . A byte string can be decoded back into a character string, if you know which encoding was used to encode it. Encoding and Decoding are inverse processes.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstate Byte Decoding
# initialising a String
a = 'Wikitechy'
# initialising a byte object
c = b'Wikitechy'
# using decode() to decode the Byte object
# decoded version of c is stored in d
# using ASCII mapping
d = c.decode('ASCII')
# checking if c is converted to String or not
if (d==a):
print ("Decoding successful")
else : print ("Decoding Unsuccessful")python tutorial - Output :
Decoding successful