Learn Python - Python tutorial - python yield - Python examples - Python programs
The yield statement suspends function’s execution and sends a value back to caller, but retains enough state to enable function to resume where it is left off. When resumed, the function continues execution immediately after the last yield run. This allows its code to produce a series of values over time, rather them computing them at once and sending them back like a list.
Let’s see with an example:
python - Sample - python code :
# A Simple Python program to demonstrate working
# of yield
# A generator function that yields 1 for first time,
# 2 second time and 3 third time
def simpleGeneratorFun():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
# Driver code to check above generator function
for value in simpleGeneratorFun():
print(value)Output:
1 2 3
Return sends a specified value back to its caller whereas Yield can produce a sequence of values. We should use yield when we want to iterate over a sequence, but don’t want to store the entire sequence in memory.
Yield are used in Python generators. A generator function is defined like a normal function, but whenever it needs to generate a value, it does so with the yield keyword rather than return. If the body of a def contains yield, the function automatically becomes a generator function.
python - Sample - python code :
# A Python program to generate squares from 1
# to 100 using yield and therefore generator
# An infinite generator function that prints
# next square number. It starts with 1
def nextSquare():
i = 1;
# An Infinite loop to generate squares
while True:
yield i*i
i += 1 # Next execution resumes
# from this point
# Driver code to test above generator
# function
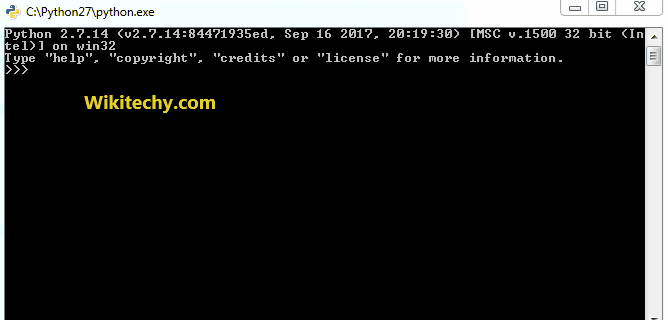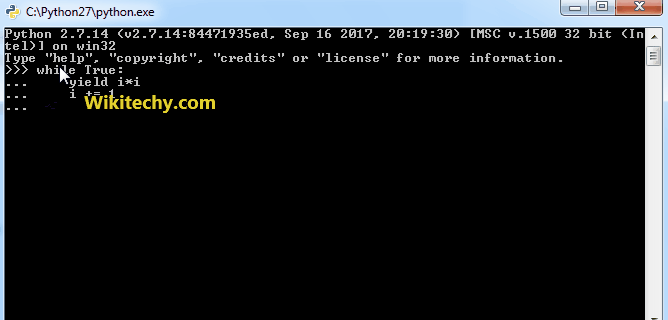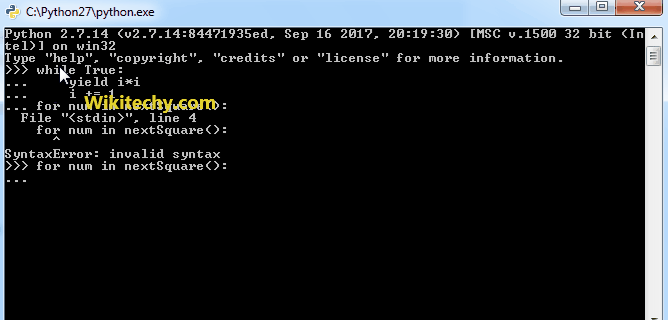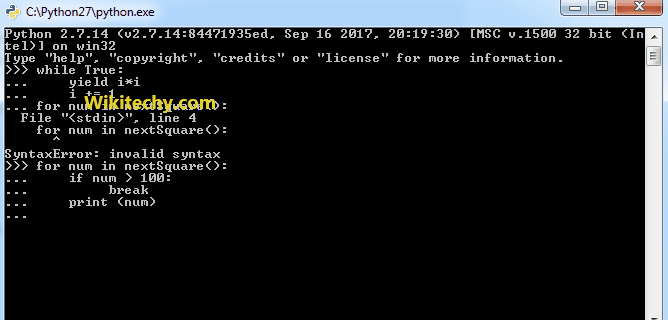
for num in nextSquare():
if num > 100:
break
print(num)Output:
1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81 100
