1. True : This keyword is used to represent a boolean true. If a statement is truth, “True” is printed.
2. False : This keyword is used to represent a boolean false. If a statement is False, “False” is printed.
True and False in python are same as 1 and 0.Example:
python - Sample - python code :
print False == 0
print True == 1
print True + True + True
print True + False + Falseclick below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
3. None : This is a special constant used to denote a null value or a void. Its important to remember, 0, any empty container(e.g empty list) do not compute to None.
It is an object of its own datatype – NoneType. It is not possible to create multiple None objects and can assign it to variables.
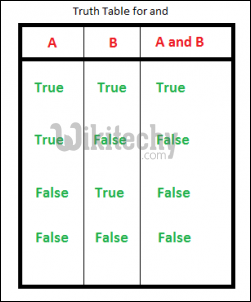
4. and : This a logical operator in python. “and” returns true if both the operands are true. Else returns false.The truth table for “and” is depicted below.
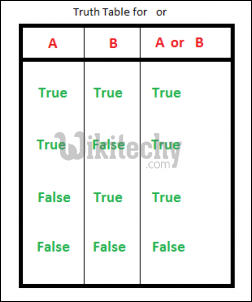
5. or : This a logical operator in python. “or” returns true if any one of the operand is true. Else returns false.The truth table for “or” is depicted below.
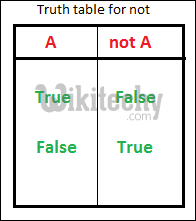
6. not : This logical operator inverts the truth value.The truth table for “not” is depicted below.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstrate
# True, False, None, and, or , not
# showing that None is not equal to 0
# prints False as its false.
print (None == 0)
# showing objective of None
# two None value equated to None
# here x and y both are null
# hence true
x = None
y = None
print (x == y)
# showing logical operation
# or (returns True)
print (True or False)
# showing logical operation
# and (returns False)
print (False and True)
# showing logical operation
# not (returns False)
print (not True)click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
python tutorial - Output :
False
True
True
False
False
7. assert : This function is used for debugging purposes. Usually used to check the correctness of code. If a statement evaluated to true, nothing happens, but when it is false, “AssertionError” is raised . One can also print a message with the error, separated by a comma.
8. break : “break” is used to control the flow of loop. The statement is used to break out of loop and passes the control to the statement following immediately after loop.
9. continue : “continue” is also used to control the flow of code. The keyword skips the current iteration of the loop, but does not end the loop.
Illustrations of break and continue keywords can be seen in the article below.
Loops and Control Statements (continue, break and pass) in Python
10. class : This keyword is used to declare user defined classes.
11. def : This keyword is used to declare user defined functions.
12. if : It is a control statement for decision making. Truth expression forces control to go in “if” statement block.
13. else : It is a control statement for decision making. False expression forces control to go in “else” statement block.
14. elif : It is a control statement for decision making. It is short for “else if”
if, else and elif conditional statements.
15. del : del is used to delete a reference to an object. Any variable or list value can be deleted using del.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstrate
# del and assert
# initialising list
a = [1, 2, 3]
# printing list before deleting any value
print ("The list before deleting any value")
print (a)
# using del to delete 2nd element of list
del a[1]
# printing list after deleting 2nd element
print ("The list after deleting 2nd element")
print (a)
# demonstrating use of assert
# prints AssertionError
assert 5 < 3, "5 is not smaller than 3"click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
python tutorial - Output :
The list before deleting any value
[1, 2, 3]
The list after deleting 2nd element
[1, 3]Runtime Error:
python - Sample - python code :
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "9e957ae60b718765ec2376b8ab4225ab.py", line 19, in
assert 5 < 3, "5 is not smaller than 3"
AssertionError: 5 is not smaller than 3click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
16. try : This keyword is used for exception handling, used to catch the errors in the code using the keyword except. Code in “try” block is checked, if there is any type of error, except block is executed.
17. except : As explained above, this works together with “try” to catch exceptions.
18. raise : Also used for exception handling to explicitly raise exceptions.
19. finally : No matter what is result of the “try” block, block termed “finally” is always executed.
20. for : This keyword is used to control flow and for looping.
21. while : Has a similar working like “for” , used to control flow and for looping.
22. pass : It is the null statement in python. Nothing happens when this is encountered. This is used to prevent indentation errors and used as a placeholder
23. import : This statement is used to include a particular module into current program.
24. from : Generally used with import, from is used to import particular functionality from the module imported.
25. as : This keyword is used to create the alias for the module imported. i.e giving a new name to the imported module.. E.g import math as mymath.
26. lambda : This keyword is used to make inline returning functions with no statements allowed internally.
27. return : This keyword is used to return from the function.
28. yield : This keyword is used like return statement but is used to return a generator.
29. with : This keyword is used to wrap the execution of block of code within methods defined by context manager.This keyword is not used much in day to day programming.
30. in : This keyword is used to check if a container contains a value. This keyword is also used to loop through the container.
31. is : This keyword is used to test object identity, i.e to check if both the objects take same memory location or not.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstrate working of
# in and is
# using "in" to check
if 's' in 'wikitechy':
print ("s is part of wikitechy")
else : print ("s is not part of wikitechy")
# using "in" to loop through
for i in 'wikitechy':
print (i,end=" ")
print ("\r")
# using is to check object identity
# string is immutable( cannot be changed once alloted)
# hence occupy same memory location
print (' ' is ' ')
# using is to check object identity
# dictionary is mutable( can be changed once alloted)
# hence occupy different memory location
print ({} is {})click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
python tutorial - Output :
s is part of wikitechy
w i k i t e c h y
True
False32. global : This keyword is used to define a variable inside the function to be of a global scope.
33. non-local : This keyword works similar to the global, but rather than global, this keyword declares a variable to point to variable of outside enclosing function, in case of nested functions.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python code to demonstrate working of
# global and non local
#initializing variable globally
a = 10
# used to read the variable
def read():
print (a)
# changing the value of globally defined variable
def mod1():
global a
a = 5
# changing value of only local variable
def mod2():
a = 15
# reading initial value of a
# prints 10
read()
# calling mod 1 function to modify value
# modifies value of global a to 5
mod1()
# reading modified value
# prints 5
read()
# calling mod 2 function to modify value
# modifies value of local a to 15, doesn't effect global value
mod2()
# reading modified value
# again prints 5
read()
# demonstrating non local
# inner loop changing the value of outer a
# prints 10
print ("Value of a using nonlocal is : ",end="")
def outer():
a = 5
def inner():
nonlocal a
a = 10
inner()
print (a)
outer()
# demonstrating without non local
# inner loop not changing the value of outer a
# prints 5
print ("Value of a without using nonlocal is : ",end="")
def outer():
a = 5
def inner():
a = 10
inner()
print (a)
outer()click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
python tutorial - Output :
10
5
5
Value of a using nonlocal is : 10
Value of a without using nonlocal is : 5